Hi, my name is David, and if you’re anything like me… you like things easy and simple.
If this is you…
I want to learn how to build AI-powered websites. But the last thing I want to do is take a whole course (blahh), sit through a 45-minute video where someone edits out all the hard parts, or watch a coding wizard breeze through things that definitely aren’t that easy in real life.
And what you really want is…
- With very little code, I want to actually talk to an AI model
- I want the code to fit in a tiny single HTML file
- And all the fluff, theory, and over-explanations can stay far, far away
If you can give me that, I’m in.
My Dilema
I’ve “vibe-coded” my way into building a handful of apps, but honestly… I had no clue what half the code was doing. So one day I just said:
Let’s start over. Let’s understand this from the ground up, the way I’ve always learned something new.
And that’s exactly what this tutorial is.
In a few minutes, you’ll see the simplest possible way to interact with Google Gemini. No installations, no setup, no build tools, no magic. Just one HTML file, a few lines of code, and a working AI request right in your browser.
Let’s make this as painless as humanly possible.
Building a “Hello World” App with the Gemini API in Your Browser
This tutorial will guide you through creating your very first web application that interacts with the Google Gemini API. We will build a simple HTML page that uses the Gemini JavaScript SDK to send a “Hello, world!” prompt to the model and logs the response directly in the browser’s developer console. This is the simplest way to get started with the Gemini API on the web, requiring nothing but a browser.
Application Overview
The final application will be a single HTML file. When you open this file in a web browser, the code you will copy/paste will:
- Import the Google Generative AI SDK.
- Initialize the AI model using your personal API key.
- Send a predefined prompt (“Hello, world!”) to the Gemini model.
- Receive the generated text response.
- Print the response to the browser’s developer console.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
- A Google Gemini API Key: You can get a free API key from Google AI Studio.
- A Modern Web Browser: Any modern browser like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Edge will work.
Security Warning: This tutorial places your API key directly in the client-side JavaScript code. This is fine for local testing, but you should never expose your API key this way in a public or production application. In a real-world scenario, you would make API calls from a secure backend server.
Step-by-Step Guide
We will create a single file named gemini_hello_world.html.
Step 1: Create the Basic HTML Structure
First, let’s create our HTML file and set up the basic boilerplate. This includes the document type, head, title, and body.
Create a new file named gemini_hello_world.html and add the following code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Simplest Gemini Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Check the developer console (F12) for the API response.</p>
<!-- Our JavaScript will go here -->
</body>
</html>Step 2: Add the JavaScript Module
To use modern JavaScript features like import and top-level await directly in the browser, we need to add a script tag with the attribute type=“module”. Add the following script tag inside the body of your HTML file.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Simplest Gemini Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Check the developer console (F12) for the API response.</p>
<!-- This script makes the API call. -->
<script type="module">
// All our code will go inside this tag
</script>
</body>
</html>Step 3: Implement the API Call Logic
Now, let’s write the core JavaScript code that will communicate with the Gemini API. We will do this in four parts inside the script tag.
1. Import the SDK
The first line of our script will import the GoogleGenerativeAI class from the SDK. We are using esm.run, a CDN that serves NPM packages as ES Modules, so we don’t need to install anything locally.
2. Add Your API Key
Next, create a constant to hold your API key. Replace YOUR_API_KEY_HERE with the actual key you obtained from Google AI Studio.
3. Write the Main Logic
We’ll wrap our main logic in a try…catch block to handle any potential errors during the API call. This code will initialize the model, send the prompt, and log the response. Because we are in a module script (type="module"), we can use the await keyword at the top level without needing to wrap it in an async function.
Final Code
After completing all the steps, your gemini_hello_world.html file should look like this. Make sure to replace the placeholder with your actual API key.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Simplest Gemini Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Check the developer console (F12) for the API response.</p>
<!-- This script makes the API call. -->
<script type="module">
// 1. Import the SDK
import { GoogleGenerativeAI } from "https://esm.run/@google/generative-ai";
// 2. Add your API key
// IMPORTANT: Replace with your actual API key
const API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY_HERE";
// 3. The main logic, which runs automatically
try {
// Initialize the model
const genAI = new GoogleGenerativeAI(API_KEY);
const model = genAI.getGenerativeModel({ model: "gemini-2.5-flash" });
// Send the prompt and wait for the result
const result = await model.generateContent("Hello, world!");
// Get the response as text
const text = result.response.text();
// Log the text to the developer console
console.log(text);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error:", error);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Running the Application
-
Save the file gemini_hello_world.html.
-
Open the file in your web browser. You can usually do this by double-clicking the file or right-clicking and selecting “Open with…” and choosing your browser.
-
Open the Developer Console. Press F12 on your keyboard (or Cmd+Option+J on Mac) to open the developer tools.
-
Check the Console tab. After a moment, you should see the text response from the Gemini model printed in the console. It will likely be a friendly greeting in response to your “Hello, world!” prompt.
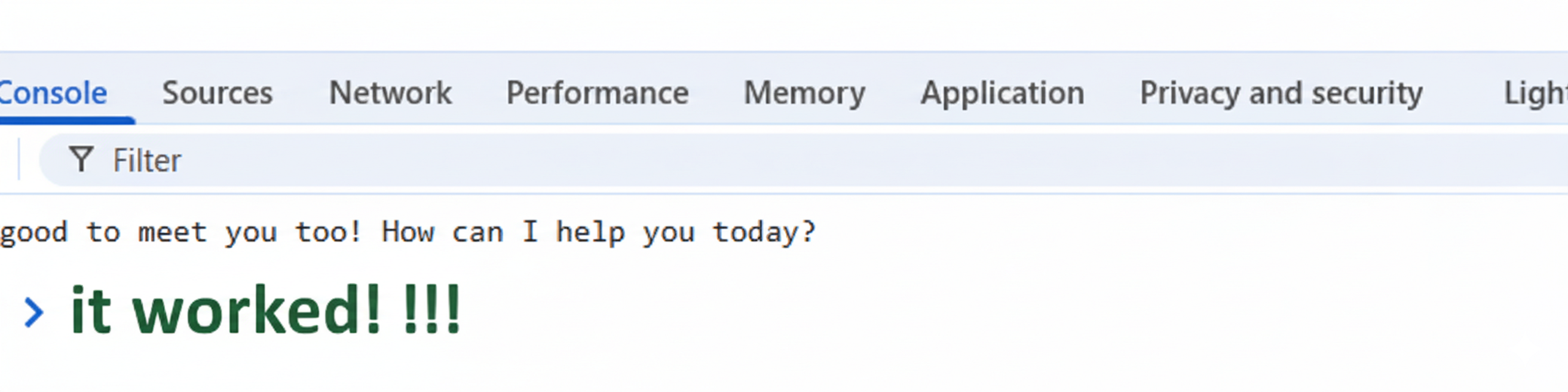
that was easy…
Congratulations! You have successfully built and run a web application that uses the Google Gemini API.